Urinary Tract Conditions
Bladder Carcinoma (Bladder Cancer)
As the name implies, bladder cancer occurs inside the bladder, within the wall of the bladder, or even on the outside of the bladder.
Common Symptoms
Some common symptoms of bladder cancer include:
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urinary urges
- Pain during urination
Diagnosis & Treatment
Treatment depends on the stage of bladder cancer, and usually, patients with bladder cancer will require an oncologist to direct their cancer care. However, certain diagnostic procedures for detecting bladder cancer are performed by urologists, including Blue Light Cystoscopy. This is an innovative diagnostic tool that helps in the diagnosis and treatment of bladder carcinoma.
Learn more about Blue Light diagnostic testing for bladder cancer detection.
Mount Sinai Medical Center is one of the few hospitals in South Florida that offers Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview, a cutting edge diagnostic tool which aids in the detection and treatment of bladder cancer.
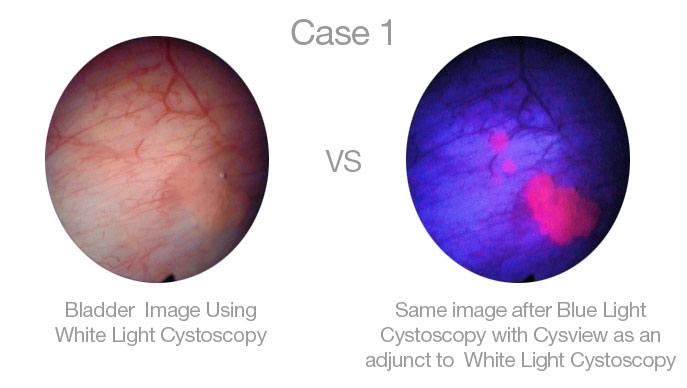
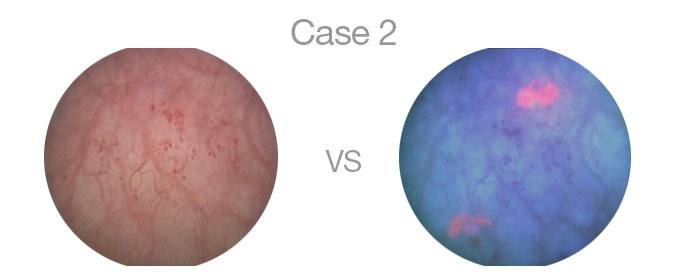
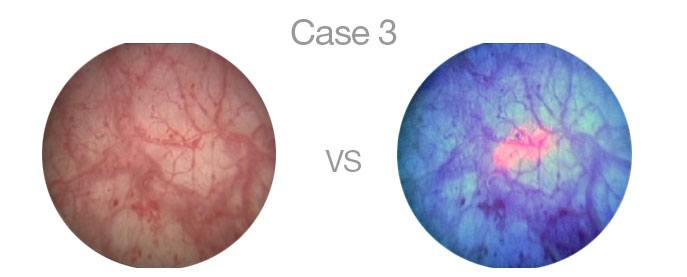
Blue Light Cystoscopy distinctively highlights cancerous tissue which under white light is not as apparent and defined. When combined with the traditional method, physicians are able to better detect and more completely remove cancerous tumors.
During the procedure an imaging solution is injected into the bladder and absorbed by cancerous tissue. After an initial standard white light cystoscopy is completed to examine the bladder, our physicians switch to the blue light which highlights cancerous tumors making them more visible and defined.
This tool, along with other detection and treatment methods, allow Mount Sinai’s Columbia University affiliated team of Urologists to offer our patients the most comprehensive and customized treatment plans for their conditions.
The images below highlight three cases of a bladder cystoscopy. The image on the left is the bladder as seen when the cystoscopy is done with White Light. The image on the right is the same image with Blue Light Cystoscopy with Cysview.
Bladder Stones
Bladder stones are made up of small, hard minerals that build up and form hard “stones” in the bladder. Concentrated urine or foreign objects in the bladder often lead to these stones.
Common Symptoms
Bladder stones may cause the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in the urine
- Difficulty in urination
- Frequent urges to urinate
The stones may pass out of the body in your urine on their own, especially by increasing fluid intake. Or, your Mount Sinai urologist may need to remove them.
Treatment Options
- Open Cystostomy – For this procedure, your Mount Sinai urologist makes a small incision in the pubic area to gain access to the urinary tract. He or she then places a large catheter into the bladder to access the stone and remove it.
- Percutaneous Suprapubic Cystolitholapaxy – With this procedure, your urologist makes a small cut in the lower abdomen and bladder to remove bladder stones.
- Transurethral Cystolitholapaxy – Your urologist uses an instrument called a cystoscope to locate the bladder stones, which are then crushed into tiny pieces and removed.
Blood In Urine
Blood in Urine, also referred to as hematuria, is a serious medical condition that your doctor should evaluate. You should immediately consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment if you see blood in your urine.
Common Causes
Some common causes of blood in urine can be:
- Bladder or kidney infection
- Bladder or kidney stones
- A blood clot or injury in the kidney(s)
- Kidney failure
- Renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer)
- Bladder cancer
Treatment Options
Treatment for blood in the urine depends completely on the underlying cause and can vary from observation, to medication, to surgery.
Cloudy Urine
Cloudy urine is not a problem in itself, but it can indicate several possible medical issues.
Common Causes
Some common causes of cloudy urine can be:
- Urinary tract infection
- The presence of bacteria, blood cells, mucus, or phosphates in the urine
Your doctor should evaluate cloudy or abnormally colored urine that is not a result of a medication or any food you’ve been eating.
Treatment Options
First, your urologist will need to diagnose the cause of your cloudy urine. Then, your physician can recommend the best treatment option – either non-surgical or surgical, depending on the medical assessment of your condition.
Cyst
A kidney cyst, or renal cyst, is a small, fluid-filled pouch that develops inside the small tubes within the kidney. Simple kidney cysts are common, usually not harmful, and may not cause any symptoms. However, cysts may become infected or begin to bleed and may require treatment.
Common Symptoms
- Blood in the urine
- Fever
- Frequent urination
- Pain in between the hip and ribs, back, or stomach, on one or either side
- Pain during urination
Treatment Options
In many cases, benign kidney cysts don’t require any treatment. However, if the cyst is placing unbearable pressure on other organs or affecting kidney function, it may need to be removed or shrunk.
Treatments include:
- Medications
- Sclerotherapy – This involves two steps: 1) removing fluid from the cyst using a long needle, and then 2) sclerosing (destroying) the lining of the cyst to prevent fluid from reaccumulating. Sclerotherapy can be performed as an outpatient procedure.
- Surgery
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination refers to the frequent need to empty one’s bladder. It is a highly inconvenient, life-disrupting condition that can be a symptom of various other diseases.
Common Causes
Frequent urination is an indication of several medical conditions, including:
- Bladder cancer
- Cystitis
- Diabetes
- Enlarged prostate
- Overactive bladder
- Prostatitis
- Tumor or mass in the pelvis
- Anxiety
- Stroke
Treatment Options
Different treatment options are available depending on the primary cause of frequent urination, and include:
- Bladder retraining
- Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor
- Medications
- Monitoring intake of fluid
Kidney Disease
The term kidney disease (or renal disease) refers to many medical conditions affecting kidney function, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney failure, renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer), kidney stones, lupus, infection, and injury.
Common Symptoms
- Anemia, caused by a build-up of waste in the blood
- Frequent need to urinate
- Lack of energy
- Loss of appetite
- Trouble sleeping
Treatment Options
- Hemodialysis is the most common treatment for kidney disease
- Kidney transplant
- Medication
The choice of kidney treatment depends on your underlying medical cause. Your physician performs detailed and in-depth medical evaluations to determine the cause and recommend a course of treatment.
Kidney Infection
A kidney infection is a bacterial infection within the kidneys. It often spreads from a bladder condition or may result from a catheter, urinary tract surgery, kidney stones, or an enlarged prostate.
Common Symptoms
- Back or groin pain
- Blood in the urine
- Fever
- Pain during urination
- Urgent or frequent urination
Treatment Options
In most cases, it is possible to treat kidney infections with antibiotics. However, severely ill patients may require hospitalization.
Kidney Pain
Patients often feel kidney pain in the back or flank. This can have several medical causes, including kidney infection, urinary tract infection, renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer), atherosclerosis (hardened arteries) of the kidney, polycystic kidney disease, and bleeding in the kidney.
Common Symptoms
You should immediately see a physician if you experience the following symptoms:
- Blood in the urine
- Body aches, including in the back or side
- Fever
Treatment Options
Your physician may test your urine to check if there are any signs of kidney infection. These tests can identify and determine the actual cause of pain. After diagnosing the underlying cause of your kidney pain, your physician prescribes the appropriate treatment, which may include medications or surgery.
Kidney Stone
A kidney stone (nephrolithiasis) is a small, hard mass of crystallized minerals that forms in the kidneys. A metabolic disorder, high calcium levels, urinary tract infections, or diuretics may cause kidney stones.
Common Symptoms
- Blood in the urine
- Extreme pain and cramping in the back and side
- Stomachache or vague pain that doesn’t seem to go away
- Vomiting or nausea
Treatment Options
In most cases, increased intake of fluid removes kidney stones. If the kidney stone is at an odd position in the kidney, or it has an unusual shape that makes it challenging to eliminate through fluids or other treatments, it may need surgical intervention called percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Other treatment options include the following:
- Shock wave lithotripsy
- Ureteroscopy
Microhematuria
Microhematuria is a shortened term for microscopic hematuria, and is unseen blood in the urine. It is usual for urine to have tiny amounts of blood in it. However, some standards can distinguish between an average number of blood cells and an abnormal number of blood cells, either in a laboratory or doctor’s office with a dipstick.
Common Causes
- Bladder cancer
- Cancer in the urinary tract lining
- Enlarged prostate
- Kidney cancer
- Kidney disease
- Kidney trauma
- Physical activity or trauma
- Prostate infection
- Urinary infection
Treatment Options
If your urine has an abnormal number of blood cells, your physician investigates the problem through various tests. Then, depending on the identified cause, the physician recommends the right treatment plan.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder is a condition that causes frequent, sudden, and unstoppable urges to urinate during the day and night. This is caused by spasms of the muscles in the wall of the bladder. It is most common in women, but does occur in men.
Treatment Options
Different options are available for treating overactive bladder, including the following:
- Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic muscles
- Medication
- Behavioral training
- Surgery
Your physician decides the treatment plan according to your specific condition, which helps improve it.
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), also known as renal kidney cancer or renal hypernephroma, is the most common kidney cancer among adults. It occurs when cells of cancer begin to uncontrollably grow within the kidney tubules lining. RCC is one of the fastest-growing cancers that often spreads rapidly to the lungs and other nearby organs.
Common Symptoms
- Appetite loss
- Blood in the urine
- Excessive growth of body hair
- Fatigue
- Lump in the abdomen
- Persistent side pain
- Unexpected weight loss
- Vision problems
Treatment Options
The standard treatments for RCC, like other cancers, include the following:
- Chemotherapy
- Immune or biological therapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
- Targeted treatment which attacks cancer cells only
Our physicians work closely with patients to diagnose and treat RCC at the early stages. We develop a personalized treatment plan depending on the stage of renal cell carcinoma to provide robust treatment.
Renal Failure
When the kidneys suddenly stop performing their function, renal failure occurs. When the kidneys lose their ability to filter toxins, they accumulate in the body, disturbing the chemical composition of your blood. This condition develops rapidly and can be a life-threatening condition. There can be several causes of renal kidney failure, including injury or damage to the kidneys.
Common Symptoms
- Shortness of breath
- Coma or seizures in severe cases
- Confusion
- Decrease in urine output, occasionally
- Fatigue
- Irregular heartbeat
- Nausea
- Pain or pressure in the chest
- Swelling in joints
- Weakness
Treatment Options
- Dialysis
- Kidney transplant
- Medications for controlling the amount of potassium in the blood and restore calcium levels
Stone Disease
Stone disease is also called kidney stone disease. In this condition, calcium deposits within the kidneys and forms hard “stones.” Inadequate fluid intake is often known to increase the risk of developing stone disease.
Common Symptoms
- Burning during urination
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Pain
Treatment Options
The stones must pass through the ureters and out the urethra, and increased fluid intake can assist this removal. Small stones don’t need any invasive treatment. However, larger stones may require more extensive procedures, including:
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
- Parathyroid gland surgery
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (surgical procedure)
Urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra. Urinary tract infection, sexually transmitted disease, injury, or sensitivity to a spermicide or sexual lubricant often causes this condition.
Common Symptoms
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent or urgent urination or discharge
- Pain during urination
- Individuals with several sexual partners or who involve in unsafe sexual practices have higher risks of developing urethritis
Treatment Options
- Medications
- Preventive measures
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the accidental release of urine. In men, this can be due to nerve problems or prostate problems.
Urinary Incontinence Types
- Functional incontinence
- Mixed incontinence
- Overflow incontinence
- Stress incontinence
- Urge incontinence
Treatment Options
Treatment for urinary incontinence depends on its type, underlying cause, and severity. In addition, you may need a combination of therapies to treat urinary incontinence. Treatments include:
- Behavioral techniques
- Electrical stimulations
- Exercises of pelvic muscle floor
- Interventional therapies
- Medications
- Surgery
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infection (UTI) or bladder infection is an infection that can occur in your urinary system. Bacteria are mainly responsible for this infection. In most cases, it affects the urethra and bladder. However, if not addressed timely, it can spread and affect the kidneys, causing serious health issues.
Common Symptoms
- Difficulty in passing urine
- Frequent urges to urinate
- Murky or cloudy urine
- Pain while urinating
Treatment Options
- Hormonal therapy
- Medications for treating simple infections
If you have a UTI history, you should discuss it with your physician, who’ll recommend the best treatment option.
Voiding Dysfunction
Voiding dysfunction refers to an inability to empty the bladder. This occurs most commonly in men over the age of 50 experiencing prostate enlargement. Infection, certain medications, constipation, or complications from surgery may also cause void dysfunction.
Common Symptoms
- Dribbling
- Frequent urination
- Pain in the abdomen, flank, or back
- Straining or pain during urination
- Urgent urination
- Urinary tract infection
Treatment Options
Your physician identifies the underlying cause and develops a suitable treatment plan, which may include:
- Bladder training
- Botox injections
- Medications
- Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS)
- Sacral nerve stimulation
- Self-catheterization
Our Physicians
- Mount Sinai Medical Center (Main Campus)
- 305.674.2499
- Mount Sinai Primary & Specialty Care Midtown
- 786.598.4560
Akshay Bhandari, MD
Co-Chief, Columbia University Division of Urology at Mount Sinai Medical Center
Director, Robotic Surgery
Assistant Professor at the Columbia University Division of Urology at Mount Sinai Medical Center
- Urology
- Cancer
- Oncology
- Robotic Surgery
- Urologic Oncology
- Mount Sinai Medical Center (Main Campus)
- 305.674.2499
- Mount Sinai Emergency Center, Physician Offices, Cancer Center and Diagnostic Center Aventura
- 305.692.1080
Alan M Nieder, MD
Co-Chief, Columbia University Division of Urology at Mount Sinai Medical Center
Program Director, Urology Residency Program
Associate Professor at the Columbia University Division of Urology at Mount Sinai Medical Center
- Urology
- Cancer
- Oncology
- Urologic Oncology
- Robotic Surgery
- Mount Sinai Medical Center (Main Campus)
- 305.674.2499
- Mount Sinai Emergency Center, Physician Offices, Cancer Center and Diagnostic Center Aventura
- 305.692.1080
- Mount Sinai Specialty Care Key West I Cardiology, Urology & Vascular Care
- 305.294.8334
Billy H Cordon-Galiano, MD
Director, Urologic Reconstruction, Trauma, and Prosthetics
- Urology
- Men’s Health
- Robotic Surgery
- Mount Sinai Medical Center (Main Campus)
- 305.674.2499
- Mount Sinai Primary & Specialty Care Skylake
- 305.919.1970
- Mount Sinai Emergency Center and Primary & Specialty Care Hialeah
- 786.584.5555
- Mount Sinai Primary & Specialty Care Midtown
- 786.598.4560